Unclear Project Scope
Struggling to define key features and deliverables? We help clarify your project scope, ensuring all requirements are identified and aligned before development begins.

Set a solid foundation for your digital product development with a team of business analysts, designers, and software development experts. With defined goals, a clear project scope, and precise technical requirements, you'll experience a smooth development process.
When to Invest in a Product Discovery Phase
Struggling to define key features and deliverables? We help clarify your project scope, ensuring all requirements are identified and aligned before development begins.
Not sure which technologies or system architecture to choose? We evaluate feasibility, select the best tech stack, and design a scalable, future-proof architecture.
Building without understanding user needs is risky. We conduct in-depth research and gather insights to ensure your product addresses real user problems and brings value.
We help estimate development costs, prioritize features, and identify potential risks early. Our proactive approach ensures your project stays on track and within budget.
Discovery in a Nutshell

Daria Lopatiukova
Lead Business Analyst
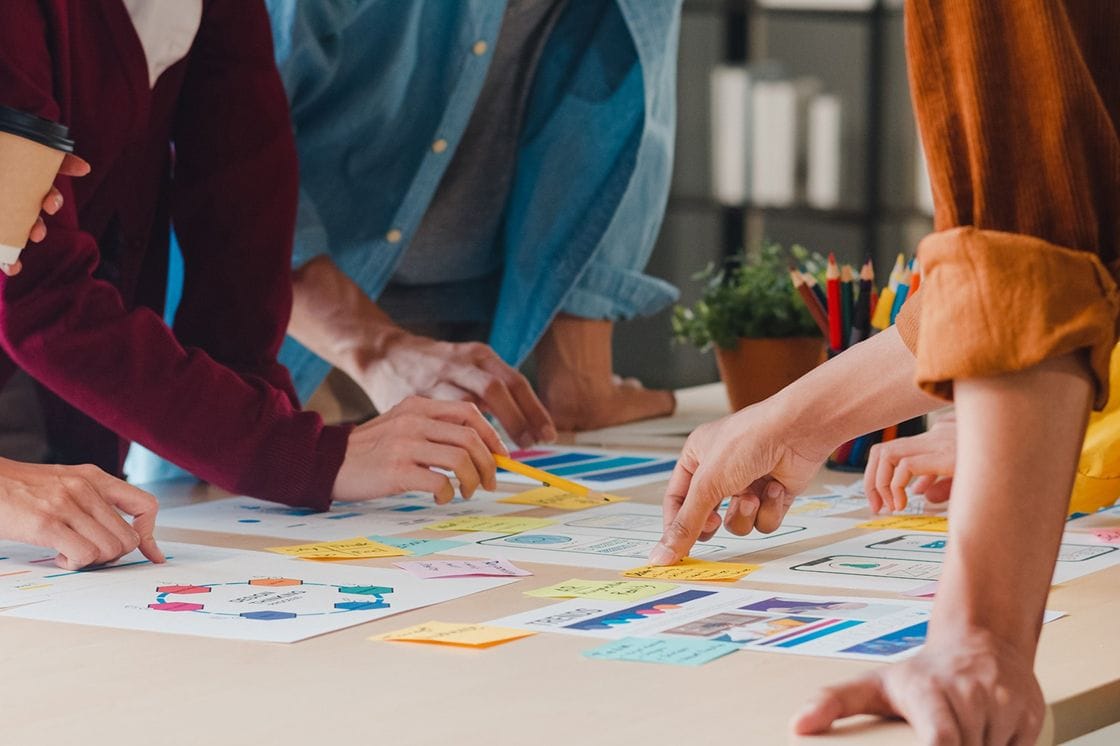
The discovery phase is a critical foundation for any development project. During this stage, the team creates key artifacts that establish a shared vision for the future product. It’s also the first opportunity for the client and development team to collaborate, align on a strategic roadmap, and gain a clear understanding — not just of the product, but of the business as a whole.
Validate your ideas with experts!
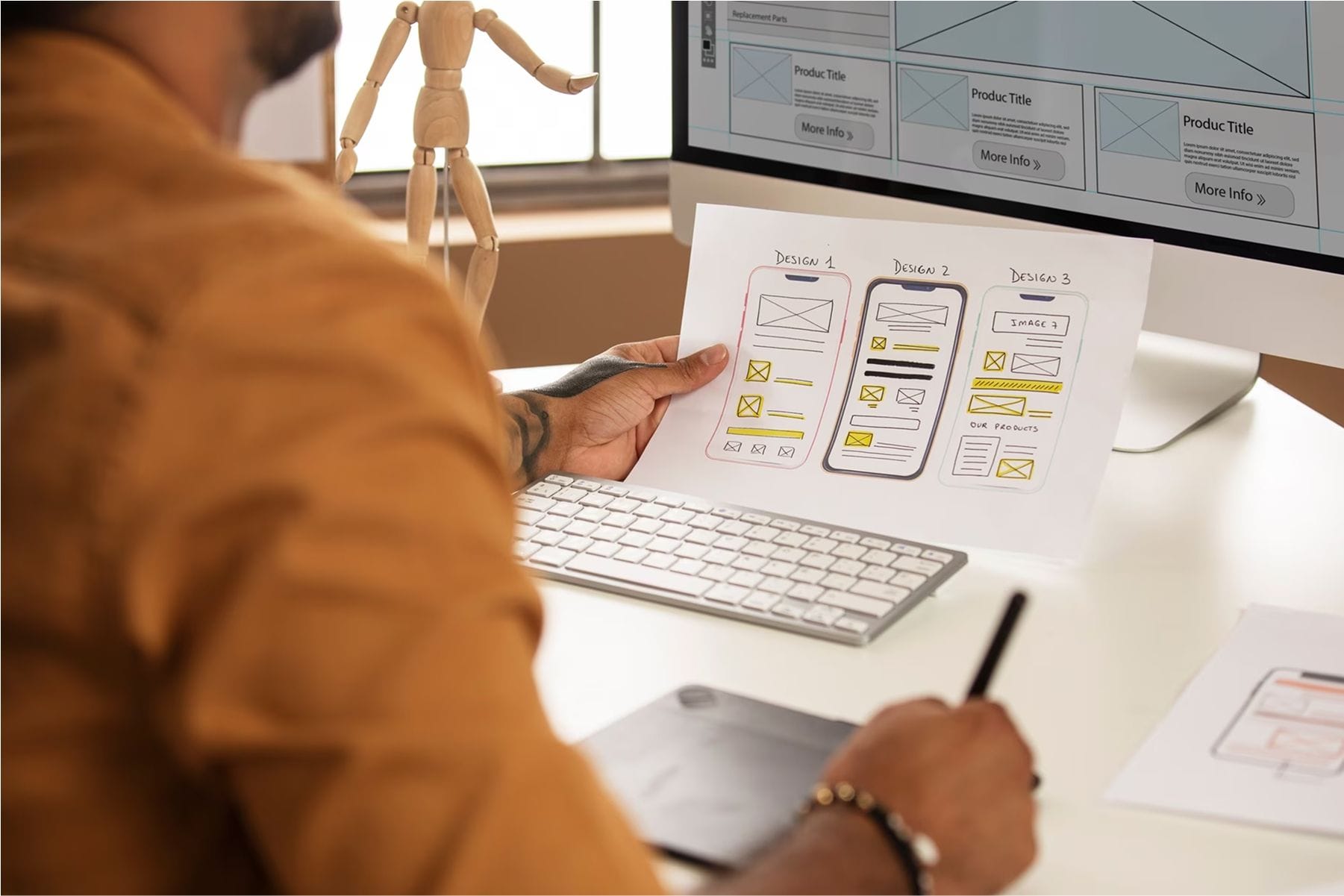
Discovery Phase Deliverables
Integrated Approach for Ultimate Success
We bring together the best of business, design, and development to ensure your project thrives at every stage.


Industry-Specific Discovery Phase Variations









How the Discovery Phase Works

Benefits of Discovery Phase
Project Clarity
Well-defined scope and goals
User Needs
Based on research and real insights
Technical Planning
Feasibility, tech stack, and risks assessed
Cost & Timeline Control
Budget and timeline estimated
Risk Management
Risks identified and mitigated early
Project Clarity
Unclear requirements, leading to scope creep
User Needs
Assumptions may lead to usability issues
Technical Planning
Higher risk of technical roadblocks
Cost & Timeline Control
Risk of delays and cost overruns
Risk Management
Unforeseen issues may arise later
Frequently Asked Questions

The discovery phase is not essential for projects that do not involve business logic. If your goal is to create a corporate website or a simple landing page, then the discovery phase might be excessive, and focusing solely on design could be sufficient. However, if your product aims to transform, automate a business process, or provide a service to your customers, the discovery phase will help identify requirements at an early stage. This not only saves time during development but also reduces overall implementation costs. As we all know, the earlier the requirements are identified and aligned, the cheaper it is to implement them.

The key to a successful project is a strong business idea backed by real market need, a solid tech solution, and a clear go-to-market plan.
